The Importance of Energy Efficiency in Ventilation Systems for Metro and Railway Tunnels

In the early 21st century, global awareness has been keenly focused on energy efficiency across various fields of application. The ongoing surge in energy consumption due to rapid industrialization and mass production processes has led to substantial environmental degradation and significant economic costs. Consequently, efforts to reduce or optimize energy consumption in any improvable process are gradually being implemented. Among these measures are advanced techniques such as implementing cutting-edge technology and complex algorithms to minimize energy expenditure.
ENERGY CONSUMPTION IN METROS AND RAILWAY
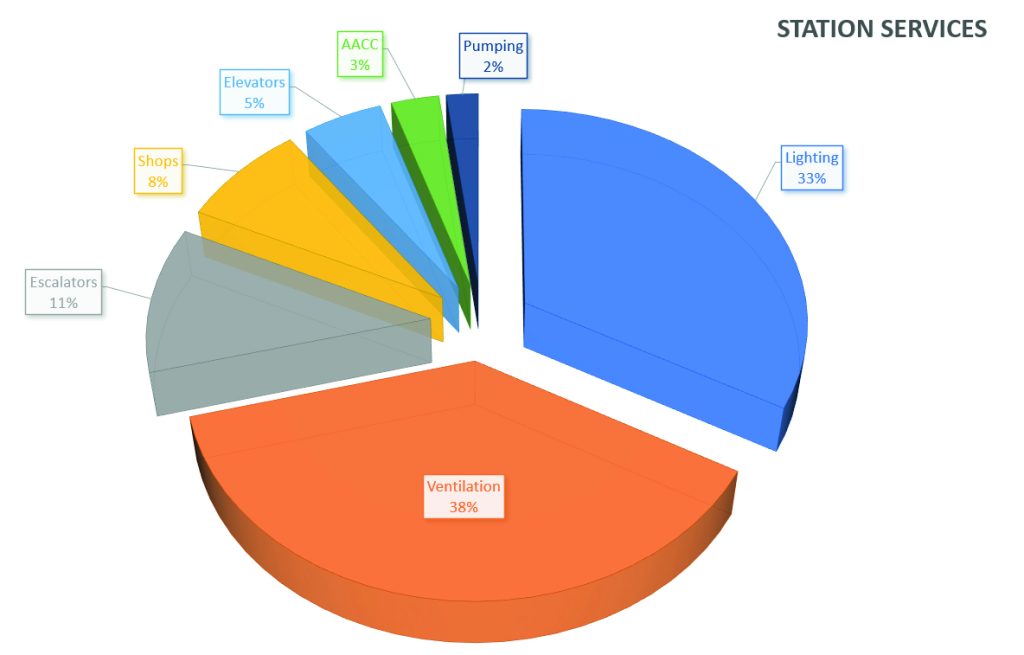
In infrastructures like metros and railways, which operate year-round to serve the public, there exists a substantial energy demand, particularly in large cities. Energy requirements in this context primarily involve two aspects: traction, representing the energy needed to move trains, and station facilities. Station facilities comprise various components, including ventilation (34% of consumption), lighting (33%), and escalators (12%).
EUROPEAN COMMISSION REGULATION 2019/1781
This regulation significantly promotes energy efficiency by establishing minimum standards for electric motors used in various applications, including fans.
For several years now, all motors must meet at least IE3 efficiency standards, and in some cases, IE2 standards (for example, when driven by variable frequency drives). As of July 2021, these exceptions have been removed, making IE3 the standard for all motors. In a later phase, starting from July 1, 2023, motors ranging from 75 to 200 kW must achieve IE4 efficiency standards.
The graph clearly illustrates the performance improvement based on energy efficiency ratings.
Ventilation fans used in metros and railway lines come in a wide range of diameters and power capacities, typically between 22 kW and 250 kW. For these power ratings, there’s an approximate 1-2% performance improvement between different efficiency classes. In simpler terms, IE4 fans are about 1-2% more efficient than IE3 fans, similar to the improvement seen between IE3 and IE2..
THE IMPORTANCE OF FAN EFFICIENCY
One critical aspect often overlooked in ventilation projects is the aerodynamic design of fans, which significantly affects energy consumption. Fans are usually defined by their flow rate and pressure, specifying basic construction features like housing material, unidirectional or reversible impellers, fire resistance, and anti-corrosion protection. While these specifications allow any fan meeting the required operating point to be installed, the power consumed during operation is often disregarded.
High-efficiency fans minimize aerodynamic losses as air circulates. They encase the motor in an inner housing, incorporate elliptical vanes, and feature a symmetrical design for optimal performance in both directions, especially for reversible fans.
Compliance with electric motor regulations is crucial, but the potential for energy efficiency improvement significantly increases with attention to fan design. Therefore, focusing on the aerodynamic design of fans is vital, as it profoundly impacts the final energy consumption.
Additional measures contributing to energy savings involve optimizing ventilation shaft architecture. Many ventilation circuits have sharp angles, constrictions, and obstacles, leading to turbulence and pressure losses, ultimately increasing fan electricity consumption. Precautions such as smoothing out angles and eliminating constrictions are cost-effective yet offer substantial energy-saving benefits.
All these aspects, including fan efficiency and shaft design, are vital considerations from the project’s outset. Thus, the involvement and coordination of all stakeholders (government bodies, operators, engineering firms, etc.) are necessary for successful implementation. Energy savings represent a shared benefit, not only in economic terms but also in environmental sustainability. Consequently, it’s imperative for everyone to contribute within their capacity.
